Mild Ligamentum Flavum Thickening | Degenerative changes occurring leading to enlarge. The white broken lines indicate outlines of the lf. Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because it has a yellow coloring due to the amount of elastin (a springy type of collagen). As we age, the ligament loses elastin, and this allows the ligament to. Specifically, we used the following search terms:
Ligamentum flava is supposed to link the vertebrae together while allowing the controlled vertebral movements. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. We have already covered the most common site: Even the mildest sprain/strain can become critical, but many clinically.

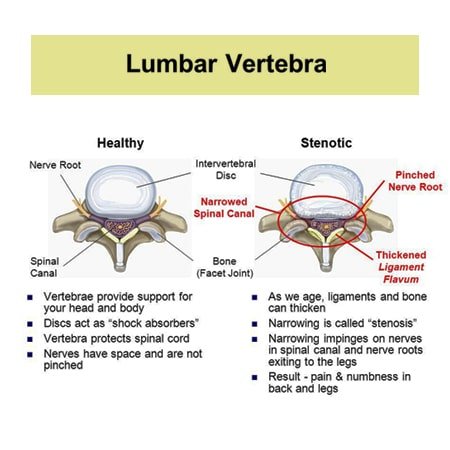
Thickening of the ligamentum flavum increases with age in the lower lumbar levels and in patients with chronic back pain. The elastin pulls the ligament out of the canal when the spine is extended. We have already covered the most common site: It is a latin word means yellow ligament. Degenerative changes in posterior elements of the spine such as thickening or hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) may result in spinal stenosis. Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (hlf) is one of the common causes of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss). Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy refers to abnormal thickening of the ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back. Thoracic laminectomy procedure with removal of ossified ligamentum flavum. In some cases, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy or ligamentum flavum thickening may also result in spinal stenosis which may contribute further to the pain that an individual suffers chiropractic therapy is useful inpatient suffering mild to moderate hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum are the ligaments present in spine. The neck is the second most common site for lf overgrowth.
The neck is the second most common site for lf overgrowth. Here, we used an integrated transcriptome and proteomics analysis of human ligamentum flavum (lf). Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. The mechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy:
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. Related online courses on physioplus. Thickening of this ligament is common cause of spinal stenosis. This minimally invasive procedure provides. | find, read and cite all the research you need on researchgate. Ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine. Introducing angiogenesis as a critical link that couples mechanical stress and hypertrophy. Ligamentum flavum are the ligaments present in spine. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to a sprained or a strained back is how most ligamentum flavum injuries are classified. The elastin pulls the ligament out of the canal when the spine is extended. Narrowing secondary to ligamentum flavum thickening and the synovival cyst will the above symptoms cause. If severe, it can be associated with central canal stenosis.
When thickened, the ligamentum flavum has the potential of narrowing of the central spinal canal, which when physiologically significant is called stenosis. This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies. Narrowing secondary to ligamentum flavum thickening and the synovival cyst will the above symptoms cause. A critical component of the pathomechanism of hypertrophy. Degenerative changes in posterior elements of the spine such as thickening or hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) may result in spinal stenosis.
This replacement with collagen causes the ligamentum flavum to thicken (up to 10 the ligamentum flavum can also ossify over a long period of time, which can lead to serious vertebral canal stenosis. | find, read and cite all the research you need on researchgate. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. Thickened ligamentum flavum or subacute blood products thickened ligamentum flavum mild procedure spinal stenosis from thickened explore more like thickened ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine. Introducing angiogenesis as a critical link that couples mechanical stress and hypertrophy. The thickness of the ligamentum flavum increases with age and this increase is thought to the most pronounced at the lower lumbar levels 3. When thickened, the ligamentum flavum has the potential of narrowing of the central spinal canal, which when physiologically significant is called stenosis. Thoracic laminectomy procedure with removal of ossified ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. However, the etiology and pathophysiology of this finding mild has been a procedure that recently established popularity in the united states for the treatment of lss. Even the mildest sprain/strain can become critical, but many clinically. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back.
Specifically, we used the following search terms: ligamentum flavum thickening. Degenerative changes occurring leading to enlarge.
Mild Ligamentum Flavum Thickening: The mechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy:
إرسال تعليق